Anaerobic COD treatment: an ecological and economical solution
Anaerobic processes for wastewater treatment are biological processes in which organic pollutants are converted into biogas in order to remove them from the wastewater. Anaerobic processes are characterized by high degradation rates, while minimizing power consumption and the volume of sludge produced.
The principle of anaerobic treatment
Wastewater contains high levels of organic matter, nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus), bacteria and pathogens. Biological treatment aims to eliminate these components through the action of various microorganisms.
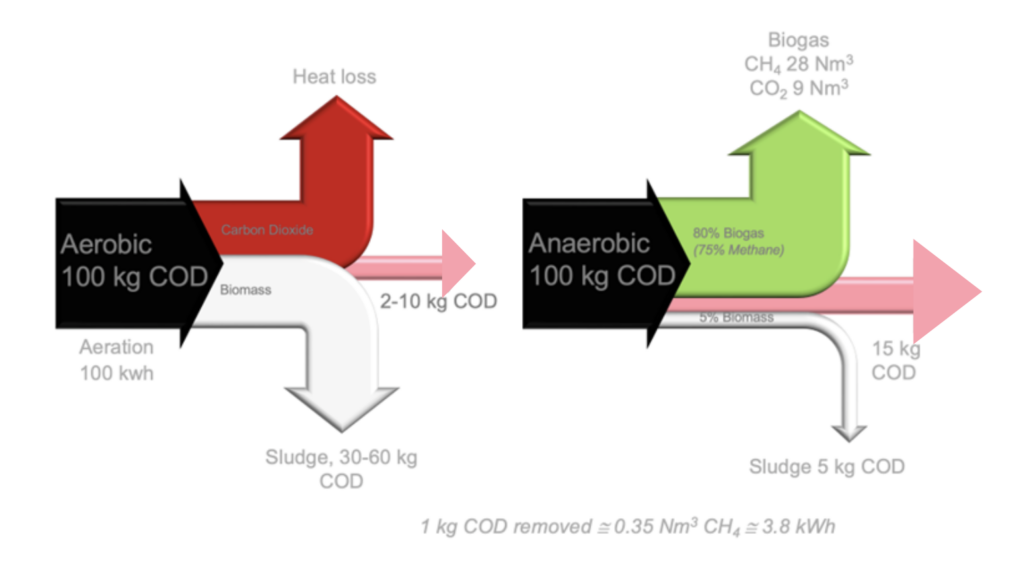
Anaerobic treatment uses microorganisms to decompose organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This natural, environmentally-friendly process transforms organic pollutants into biogas, mainly composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The biogas produced can then be converted into energy, making it a doubly beneficial solution: reducing pollutants and producing renewable energy.
The advantages of anaerobic treatment
- Economical and ecological: Anaerobic treatment is more economical than many mechanical or chemical processes, yet highly effective in degrading organic matter.
- Energy recovery: The biogas generated can be used to generate electricity or heat, or injected into the natural gas network after treatment.
- Sludge reduction: This process produces less sludge than aerobic treatments, reducing waste management costs.
- Environmentally-friendly: By minimizing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, anaerobic treatment contributes to environmental protection.
Technologies used
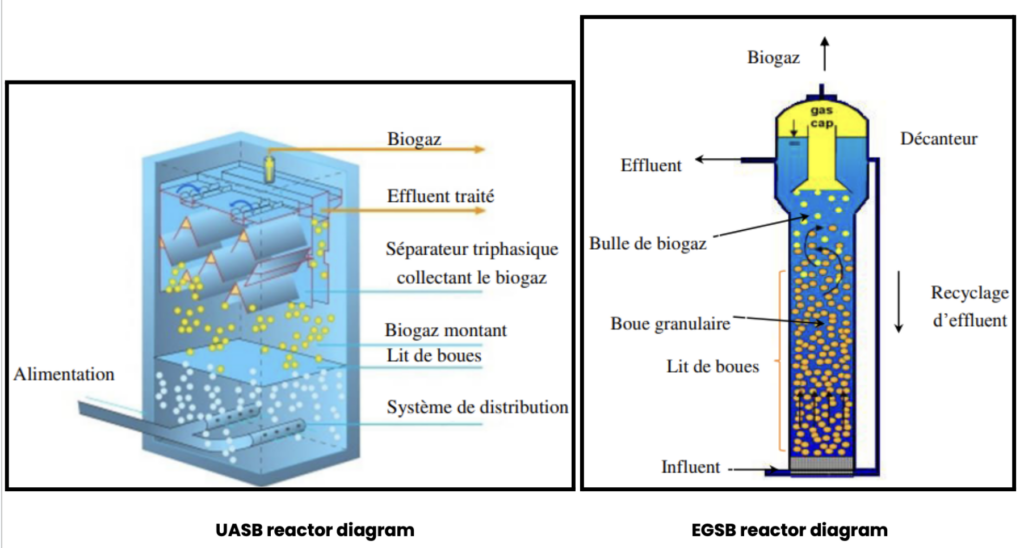
Reactor types
- UASB (Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket) reactors: Widely used (80% of reactors), these reactors promote good contact between wastewater and biomass due to natural turbulence. They are efficient and reduce operating costs.
- EGSB (Expanded Granular Sludge Bed) reactors: Suitable for treating toxic or recalcitrant effluent due to improved effluent distribution and efficient recirculation. They can operate with low hydraulic residence times and high volume loads.
Biogas valorization
Biogas, composed mainly of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), can be valorized in several ways to avoid contributing to the greenhouse effect:
- Cogeneration: high-efficiency combined production of electricity and heat.
- Gas injection: After advanced treatment, biogas can be injected into natural gas networks.
- Heat recovery: Use of recovered heat for various industrial and domestic applications.
Conclusion
Anaerobic wastewater treatment represents an innovative and sustainable solution for industrial effluent management. By transforming organic matter into valuable biogas, this process offers an ecological and economical alternative to traditional methods. Our company, at the forefront of this technology, offers solutions optimized to meet the specific needs of each industry, guaranteeing high performance and reduced operating costs.
To find out more about our anaerobic treatment solutions and discover how we can help you improve your wastewater management, don’t hesitate to contact us.
Source : Oseido traitement anaérobie

